Metal-center proteins
This research focus initially began with the ability of flavonoids to directly bind redox metals, and evolved into discovering the roles of flavonoid-sensitive metal-centered proteases in plant development and the potential of metal accumulating plants to benefit society. The current basic research in my lab is on the cupin AUXIN BINDING PROTEIN 1 in auxin homeostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum, and DAO, the 2-oxoglutarate FeII-dependent dioxygenase family in auxin homeostasis. The current applied research is on biofuels and iron nutrition in rice and soybean.
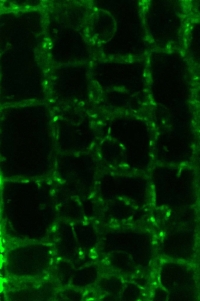
A fluorescent auxin analogue in the endoplasmic reticulum of a plant root
M1 aminopeptidases
APM1 loss-of-function mutants show distinct developmental defects in embryogenesis and seedling development, indicating that APM1 function is required at two distinct times during development. We were able to separate these function by using inducible silencing of APM1 in wild type at different stages to phenotype the mutant defects and inducible expression of APM1 in the mutant to rescue the defects.
M24 aminopeptidases
APP1 loss-of-function mutants grow more slowly than wild type, whereas gain-of-function mutants grow more quickly. The altered auxin accumulations in these mutants, suggests that APP1 may be involved in a rate limiting step regulating growth.
IAA and IAA metabolite concentrations in 7-d-old Col-0 (wild type) and dao mutant seedlings. Data are means ± SD of at least four biological repeats. Different letters indicate statistical significance (ANOVA; P < 0.05). FW, fresh weight. From Zhang et al., 216 PNAS